free and forced convection lab report
The wall temperature 𝑇 𝑊 takes the temperature value of the first thermocouple. Heat is lost in the system and calculations are shown later in the report to analyze this for the two trials in the experiment forced and free convection.

Doc Heat Transfer Final Report Melisa Irmak Academia Edu
In the next section of the report the procedure used to complete the actual.

. Convection is a mode of heat transfer caused by contact and fluid movement. In addition another target is to demonstrate the effect of the. Free or natural and forced convection.
Thermocouples measure the air temperature upstream and downstream of the surface and the temperature at the heat transfer surface. FORCED AND FREE CONVECTION 101 Introduction A key factor in convection is the heat the heat transfer coefficient h. Lab report Free Forced Convection Heat Transfer Mahmood Mohsin AL-Khusaibi 85135 Amur Sultan Al-Habsi 86260 Rashid Nasser Al Shabibi 85362 Aim.
3 INTRODUCTION- The experimental system uses a boiler which supplies heat to the water to create steam. In the experiment students take direct. Convection setup results in an increase in dissipated heat in the exiting of the fluid into the.
To Demonstrate the Relationship Between Power Input and Surface Temperature in ForcedConvection. For forced convection tests a variable-speed fan draws air up through the duct and across the surface. Edgar Clausen and William Penney.
Laboratory DemonstrationsExperiments In Free And Forced Convection Heat Transfer Author. Forced Convection Full-Technical Lab Report 1. Experiment in a thermal fluids laboratory course.
This results in a larger total heat transfer for the forced convection than the. Forced convection is a mechanism or type of heat transport in which fluid motion. Convection refers to the transfer of thermal energy in the means of diffusion.
The convection coefficient is taken to be a constant along the entire length of the fin and is an average. Work is free of mathematical errors arithmetic algebra calculus etc 6. 𝜃 𝑇𝑇 𝑇 𝑊 𝑇 2 The variable m is a ratio of parameters often used to characterize fins has units of 1m and is.
Forced Convection Heat Transfer Convection is the mechanism of heat transfer through a fluid in the presence of bulk fluid motion. Below will follow the theoretical aspects of both forced. In the forced convection the fluid to be heated is blown or pumped past the heated surface by employing a pump or a fan while in the natural or free convection fluid flow is naturally achieved based.
In addition another target is to demonstrate the effect of the fluid speed on. On increasing the wind speed the copper rod cools faster 2. Heat Transfer Lab report Free Forced Convection Heat Transfer Mahmood Mohsin AL-Khusaibi 85135 Amur Sultan Al-Habsi 86260 Rashid Nasser Al Shabibi 85362 Aim.
Heat convection plays a very important role in numerous engineering applications. All required elements of a full technical report are present. To gain a working knowledge of the hot film anemometer.
The results from pin fins made of copper aluminum and stainless steel showed. In conclusion to the experimental result the following points can be noted. Furthermore in free convection the fluid motion is caused by means such as gravity buoyancy rise and fall of warmer can cooler fluid respectively etc and in forced convection the flow of fluid is forced over a surface or in a tube through internalexternal means fans pumps etc.
For example when water is being. Instead of determining h we determine the Nusselt number Nu which a dimensionless heat transfer coefficient. The problem of simultaneous heat and mass transfer in laminar free convection from a vertical flat plate is investigated theoretically.
We have developed an experiment in free convection for MECE 352 adapted from one used in the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engi neering at The State University of New York at Buffalo SUNY Buffalo with permission. In natural convection the motion of the fluid is not created by any external force or sources. Pin Fin Lab Report Example Names ME331 Lab 04122017.
Division it is subdivided into free and forced convection. To Demonstrate the Relationship Between Power Input and Surface Temperature in Free Convection 2. As a fluid moves around the boundaries of.
The objective of this experiment to investigate the use of extended surface to improve heat transfer through surfaces. Convection is the movement of molecules within fluids ie. There is a title page with complete abstract λ b.
Capabilities Of The Free and Forced Convection Unit 1. Abstract The purposes of this experiment are to determine pin fin effectiveness and convective heat transfer coefficients for free and forced convection over pin fins of differing length and material. For free convection tests the heated air rises from the surface and up the duct.
Whenever it is difficult or not possible to determine the Nusselt number analytically. Free and Forced Convection from a Heated Cylinder. Convection is classified as natural or free and forced convection depending on how the fluid motion is initiated.
Convection is one of the major modes of heat transfer and mass transfer. It cannot take place in solids since either bulk current flows or significant diffusion can take place in solids. The objective of this experiment to investigate the use of extended surface to improve heat transfer through surfaces.
To Demonstrate the use of Extended Surfaces to Improve Heat Transfer From the Surface. There are two kinds of heat convection. There is an accurate table of contents and accurate lists of tables and figures λ c.
An integral method is used to find solutions for zero wall. To make fundamental measurements of both free and forced convection heat transfer along with measurements of flow velocity and turbulence intensity. Armfield HT19 Free and Forced Convection Heat Transfer 12 Procedure 121 Natural convection To make natural convection firstly the plate was heated up by the resistance with 8 12 15 and 20 volts respectively.
This experiment shows how the heat transfer rate changes under the circumstances of forced convection. After the system was got steady state condition each values from the T1 to T8 were noted. The thermal coefficient increases with the increase in Reynolds number 3.
In natural convection any fluid motion is.
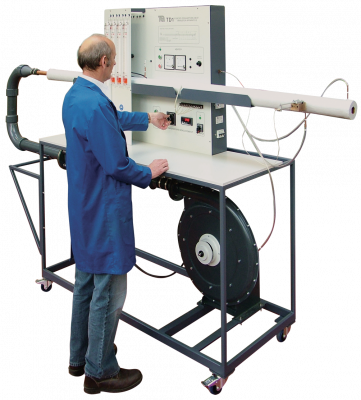
Forced Convection Heat Transfer Tecquipment
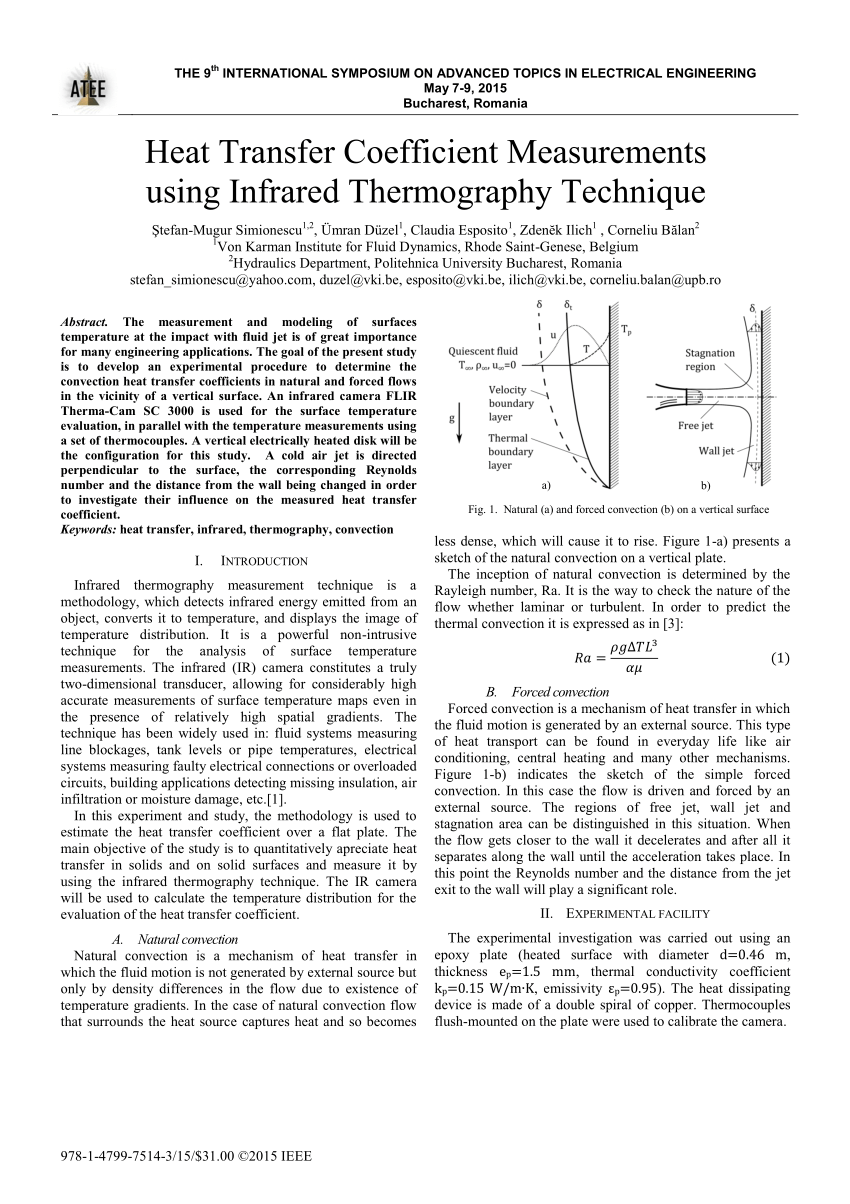
Natural A And Forced Convection B On A Vertical Surface A B Download Scientific Diagram

Pdf Free Convection Heat Transfer Coefficient

Pdf Turbulent Forced Convection
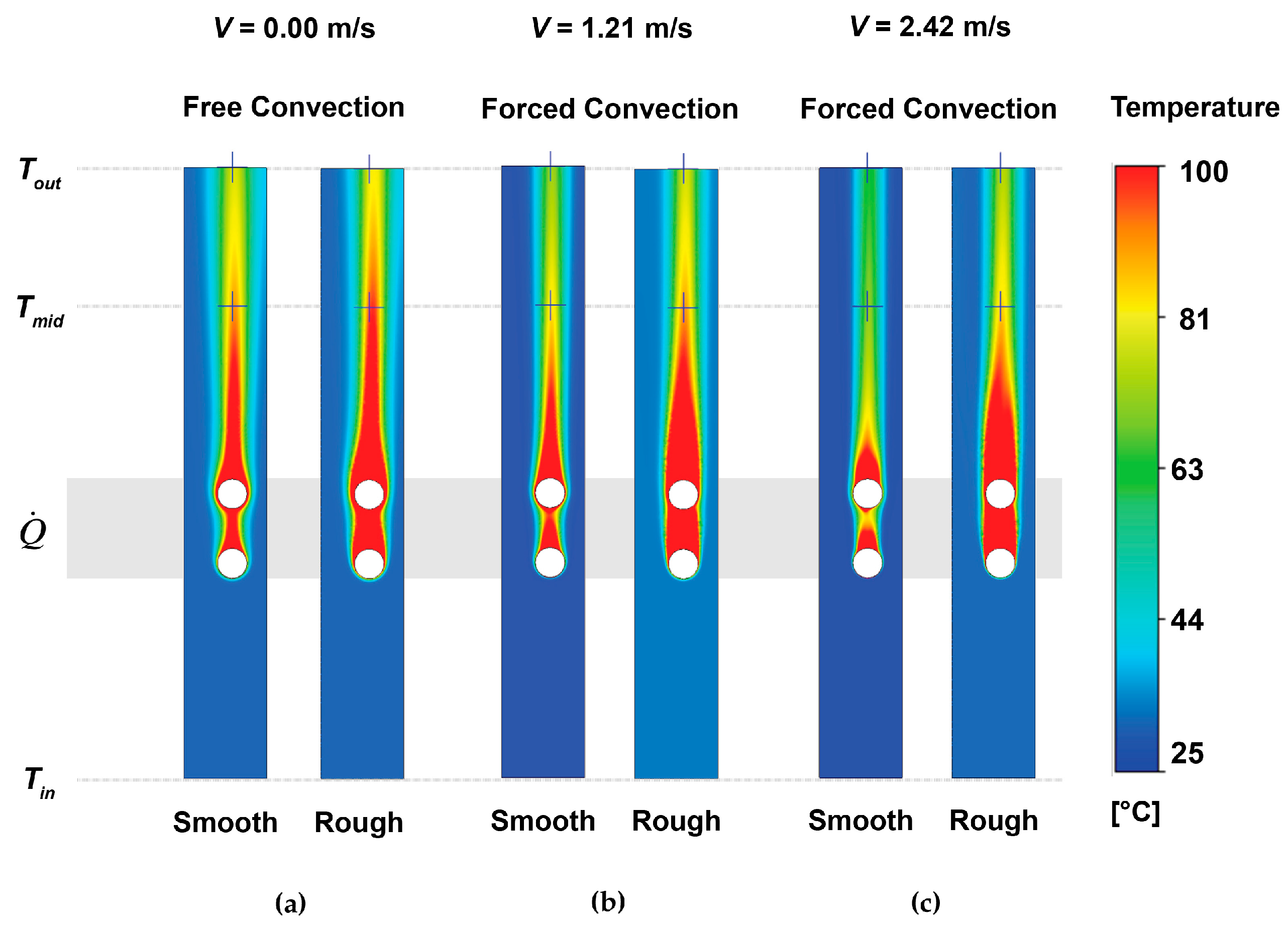
Coatings Free Full Text Heat Transfer Enhancement By Shot Peening Of Stainless Steel Html

Pdf Simplified Analytical Models For Forced Convection Heat Transfer From Cuboids Of Arbitrary Shape

Pdf Forced Convection Heat Transfer Using Water Ethylene Glycol 60 40 Based Nanofluids In Automotive Cooling System

Final 201 Thursday A 3 Convective And Radiant Heat Transfer
Natural A And Forced Convection B On A Vertical Surface A B Download Scientific Diagram

Pdf Analytical Modeling Of Forced Convection In Slotted Plate Fin Heat Sinks

Schematic Diagram Of The Forced Convection Apparatus Download Scientific Diagram

Pdf Forced Convection Heat Transfer Using Water Ethylene Glycol 60 40 Based Nanofluids In Automotive Cooling System

Final 201 Thursday A 3 Convective And Radiant Heat Transfer

Final 201 Thursday A 3 Convective And Radiant Heat Transfer

Natural A And Forced Convection B On A Vertical Surface A B Download Scientific Diagram

Exp6 Free Convection Surface Comparisons Pdf Experiment 6 Free Convection Surface Comparison Safety Regulations 1 Install The Apparatus In A Course Hero
